Welcome!







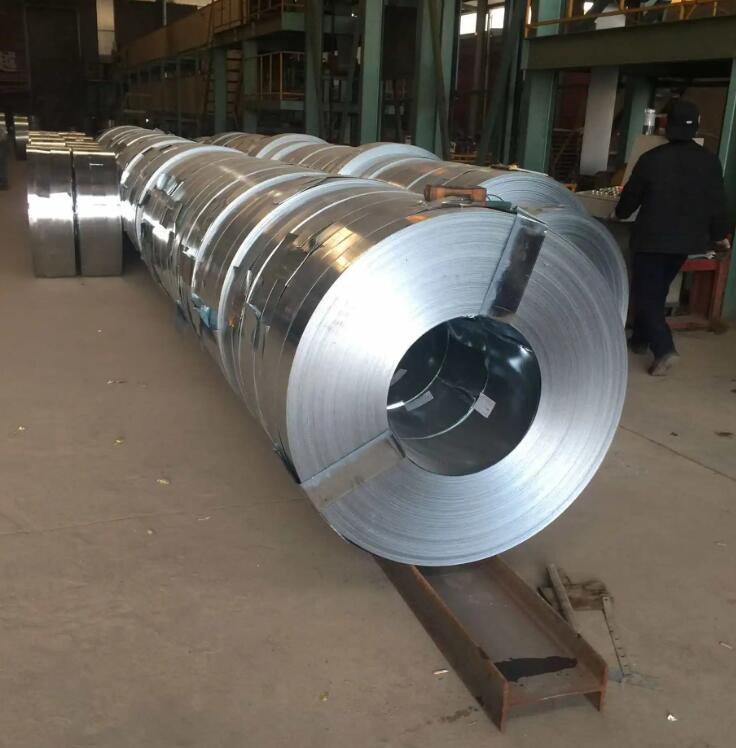
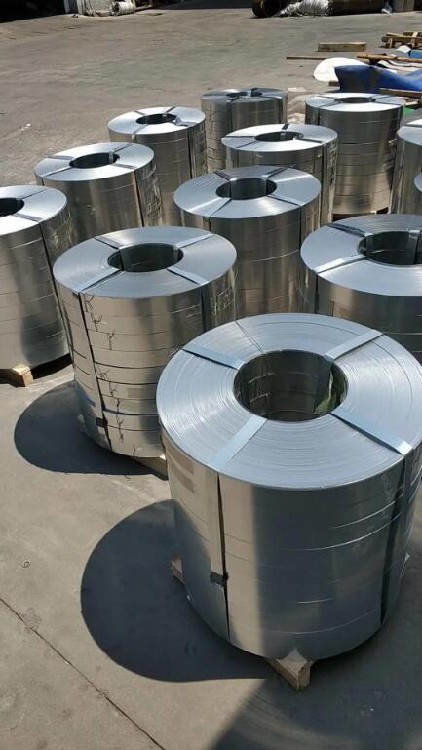
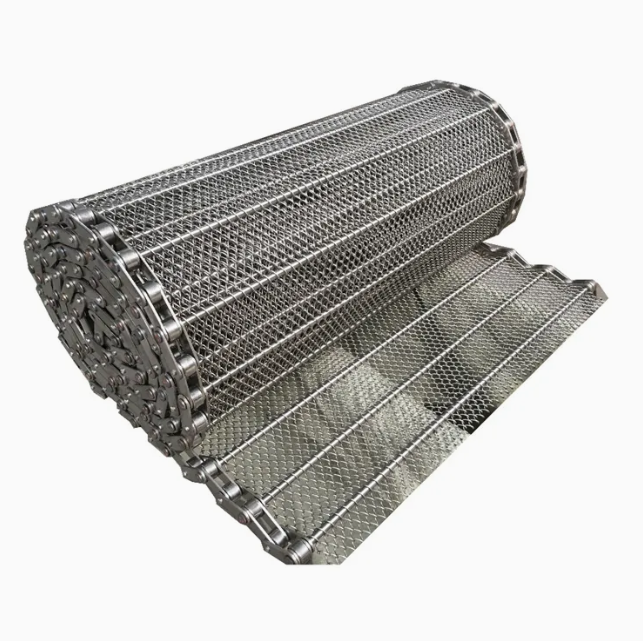
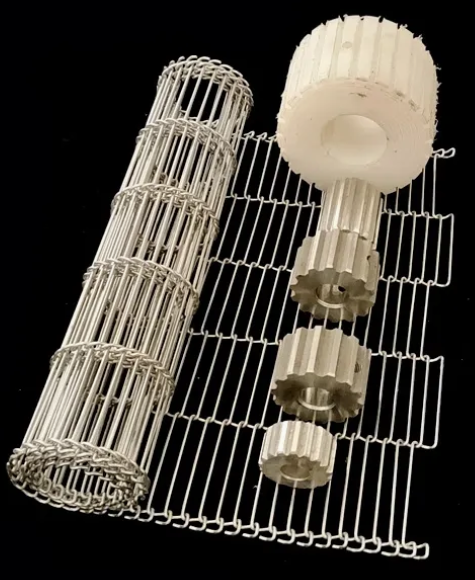
304 stainless steel belt
Product Description
304 stainless steel belt

304 stainless steel is a universal stainless steel material with stronger anti-rust performance than 200 series stainless steel materials. It is also relatively good in high temperature resistance, which can reach 1000-1200 degrees. 304 stainless steel has excellent stainless corrosion resistance and good intergranular corrosion resistance. 304 (18Cr-8Ni) material: As a widely used steel, it has good corrosion resistance/heat resistance, low temperature strength and mechanical properties; good hot processing properties such as stamping/bending, no heat treatment hardening phenomenon (non-magnetic, easy to use temperature -196℃~800℃).
304 stainless steel strip properties
Tensile strength 620 MIN
Yield strength 310 MIN
Elongation (%) 30 MIN
Area reduction (%) 40 MIN
Density of 304 stainless steel 7.93 g/cm3
Austenitic stainless steel generally uses this value
304 chromium content (%) 18--20 .
304 is equivalent to China's 0Cr19Ni9 (0Cr18Ni9) stainless steel
This stainless steel is used in a variety of fields such as household items (such as tableware, cabinets, pipelines, water heaters, boilers, and bathtubs), automotive parts (such as wipers, mufflers, and molded products), medical equipment, building materials, chemicals, food industry, agriculture, and ship component manufacturing.
304 stainless steel has advantages including excellent stainless corrosion resistance, good intergranular corrosion resistance, high strength, good high temperature resistance, good processing performance, wide range of applications, etc.
304 stainless steel is a universal stainless steel material with excellent stainless corrosion resistance and good intergranular corrosion resistance. It has strong corrosion resistance to oxidizing acids (such as nitric acid below boiling temperature with a concentration of ≤65%), and also has good corrosion resistance to alkaline solutions and most organic and inorganic acids.

The difference between 316 and 304
The two most commonly used stainless steels are 304 and 316 (or 1.4308 and 1.4408 corresponding to the German/European standard). The main difference between 316 and 304 in chemical composition is that 316 contains Mo, and it is generally recognized that 316 has better corrosion resistance and is more corrosion-resistant than 304 in high temperature environments. Therefore, in high temperature environments, engineers generally choose 316 parts. But there is no absolute. In a concentrated sulfuric acid environment, no matter how high the temperature is, don't use 316! Otherwise, this will be a big deal. Everyone who studies mechanics has learned about threads. Remember that in order to prevent the threads from biting at high temperatures, a black solid lubricant needs to be applied: molybdenum disulfide (MoS2). From it, two conclusions are drawn: 1. Mo is indeed a high-temperature resistant substance (Do you know what crucible is used to melt gold? Molybdenum crucible!). 2. Molybdenum easily reacts with high-valent sulfur ions to form sulfides. Therefore, no stainless steel is super corrosion-resistant. After all, stainless steel is just a piece of steel with more impurities (but these impurities are more corrosion-resistant than steel^^), and steel can react with other substances.
Compared with ordinary stainless steel, the composition index of food-grade 304 stainless steel is more stringent, mainly containing 18%-20% chromium and 8%-10% nickel, which ensures its wide application in the food and medical industries. 304 stainless steel also has good welding performance and hot processing performance such as stamping and bending, no heat treatment hardening phenomenon, and a wide range of operating temperatures, from -196℃ to 800℃.
| Steel Grade | Density(g/cm3) |
| Steel No. | density |
| 304,304L,305,321 201,202,301,302 | 7.93 |
| 316,316L,347 309S,310S | 7.98 |
| 405,410,420 | 7.75 |
| 409,430,434 | 7.7 |
Recommended Products
Recently Viewed
Contact Us
Qingzhou Jianfu Gear Co., Ltd.